Dear readers, do you know that San Pablo City has seven lakes? Allow Tita S to tell you 12 facts about them.
1.The City of San Pablo1 is located in the province2 of Laguna3, in the Calabarzon4 region5, in the island group of Luzon6, Philippines.
2. The 7 crater lakes are scattered all around the city. That is why it is called “The City of Seven Lakes”.

Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/7-Lakes-of-San-Pablo-City-Laguna-356649184395237/photos/a.356650911061731/356651074395048
3. The lakes are maars7, or low profile volcanic craters, located in the San Pablo Volcanic Field8. They are among the 200 small monogenetic9 volcanoes found along the Macolod Corridor10, a rift zone11 between Mount Makiling12 and Mount Banahaw13, which is part of the larger Southwestern Luzon Volcanic Field14.
The craters were formed by a unique process called phreatic eruption14 where shallow lava from Mount San Cristobal15 intersected groundwater which blew out (steam-heated eruption) the overlying rocks to form a circular and crater-like depression that eventually filled-up with rainwater. The varying depths of these lakes, which are from 7 m to 156 m, suggest a volcanic origin.
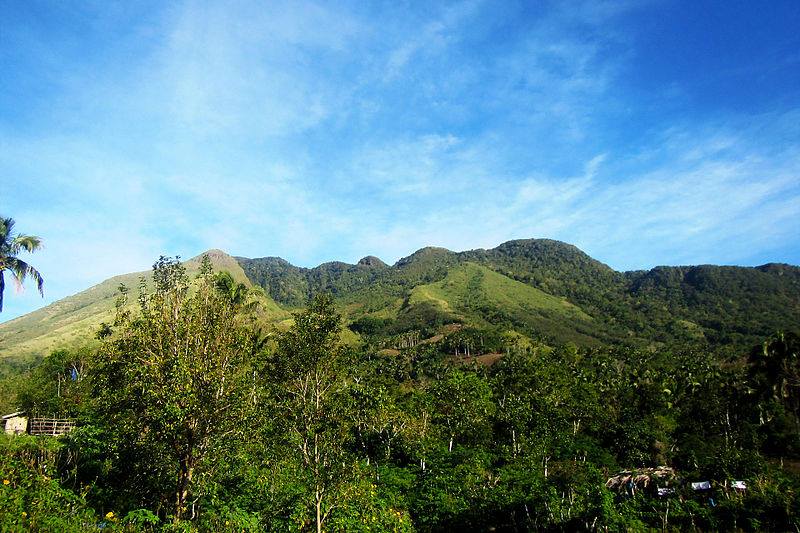

Mt. San Cristobal – Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/1150651761686320
4. The first lake is Lake Bunot, a crater lake located in Barangay Concepcion, 4.5 km (2.8 mi) from the city proper. It has a normal surface area of 30.5 ha (75 acres), with a maximum depth of 23 m (75 ft). It is known for cultured tilapia in fishpens from where most of the residents derive their income.
Lake Bunot – Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/a.1124214957663334/1124281297656700 post
There is a legend to the name of this lake – bunot (coconut husk). It is said that in the Spanish Era (1565 – 1898), some Spanish soldiers went to this lake for surveying purposes and inquired about the lake’s name from a man husking coconuts by the shore. The latter misunderstood, thinking the soldiers were asking for the name of the coconut husk in their dialect, and replied in Tagalog – bunot. The Spaniards left, believing that the name was Lake Bunot.
Lake Bunot is closest to Lake Sampaloc (the largest lake, at the center of the city; see fact 8) and is surrounded by houses.
5. The second lake is Lake Calibato or Lake Kalibato. This crater lake is located in Barangay Sto. Angel. It has an area of 42 hectares (100 acres), and an average depth of 156 m (511.811 ft).

Lake Calibato – Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/1126268460791317 post
It is the deepest recorded lake among the 7 lakes. It has a maximum capacity of about 29,600 cubic meters (1,050,000 cu ft). Its supplies San Pablo City1 and nearby towns with abundant fish (like tilapia16) and aquatic plants.
You need to trek for about 15 minutes and pass through a small brook before you get to this lake.
It was told that there was a valley in the area of this lake that was allegedly inhabited by a fairy (diwata) who wanted to keep her realm free from the intrusion of mankind. She got angry when people built rocky pathways that criss-crossed her valley. She eventually caused a strong earthquake and a severe storm that transformed the valley into a lagoon. The following morning, the villagers were awed by the body of water and called it Lake Calibato – cali, taken from the corruption of the Spanish word called for “street”, and bato – the Tagalog word for “rock”.
6. The third lake is Lake Mohikap, Lake Muhicap or Lake Mojicap. It has a surface area of 14.5 hectares (36 acres), a surface elevation of 80 meters (260 feet), a maximum length of 530 m (1,740 ft), and a maximum width of 490 m (1,610 ft). It is located in Barangay San Buenaventura and is one of the main suppliers of water in San Pablo City1. It is also a breeding area for shrimps, and is, likewise, a major source of tilapia16 for Metro Manila and suburbs.
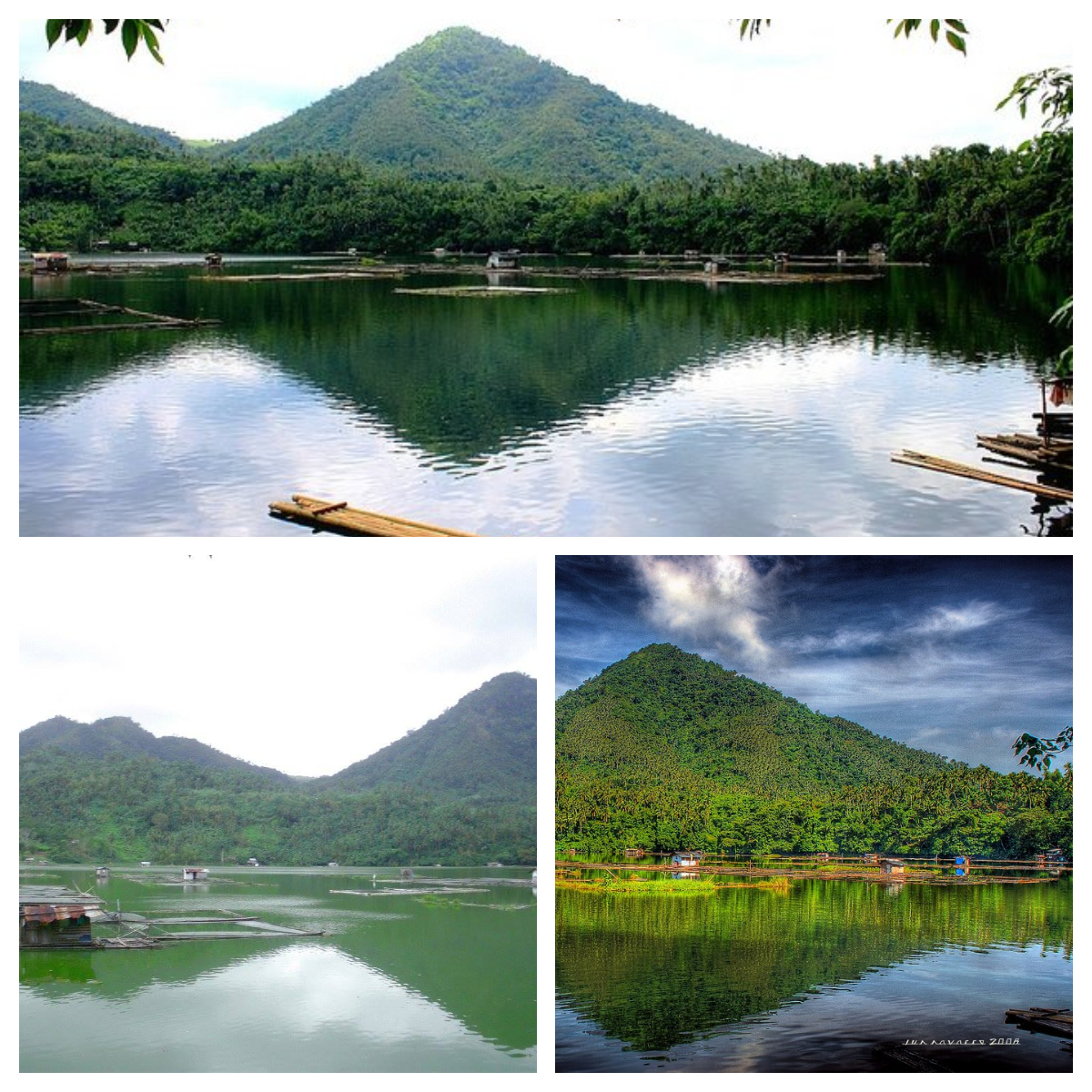

Lake Mohikap – Sources of photos: https://www.facebook.com/7-Lakes-of-San-Pablo-City-Laguna-356649184395237/photos/a.356653811061441/356653817728107 and https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/
Legend goes that a couple had a very sickly daughter named Munica and they frequently prayed to God for her health. They promised to do anything if God granted their prayer on condition that Munica must not set foot on soil. She grew up to be healthy and very industrious. One day, she sewed a dress and a ball of thread fell on the ground. She tried to retrieve it, she fainted and fell. She sank with the entire neighborhood, and the lake formed. So, the lake was named after her industriousness in the local dialect, mahikap.
After paying PHP10 per person as entrance fee, you would have to descend 105-steps to see this lake, and you’ll also see mountains in the background. You can then rent a raft to get to the other side of the lake, and swim in shallower water. There are different sizes of bamboo rafts, from 1-2 persons (PHP300 total) to 7-12 persons (PHP120/pax)
You can also rent fishing equipment to catch fish like tilapia16 or catfish (hito). The fishing bamboo raft for 4 persons is PHP300 for 7 hrs.
7. The fourth lake is Lake Palakpakin, Lake Palacpaquin or Lake Palacpaquen. It is also located in Barangay San Buenaventura, just like Lake Mohikap. It has an area of 43 ha (110 acres) and a maximum depth of 7.5 m (25 ft).

Lake Palakpakin – Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/a.1124214957663334/1124286890989474 post
It is the shallowest among all the 7 lakes. Residents, with houses around the lake, rely on income from fishpens and fish cages that grow cultured tilapia16 and silver carps.
There is a legend that a few kilometers from San Pablo City1 was a village with an ancient tree which had a hollow trunk, called Palakpak. On moonlit nights, villagers could see a beautiful red-haired lady washing her long hair using the hollow trunk as her wash basin. There was also a river nearby where a big fish appeared each night when the beautiful lady was around.
One day, a stranger came to the village and tried to solve the mystery of the lady and her fish. So, on a moonlit night, he waited for her and approached her. Suddenly, there was thunder and lightning. There was a severe earthquake, the river swelled, and formed a lake. From then on, the lake produced a large quantity of shrimps, which when cooked, turned red. People called the lake Palakpakin, after the ancient tree, and the shrimps which gave the main source of livelihood to the local folks, they called Hipong Palakpakin or Palakpakin Shrimp.
8. The fifth lake is Lake Sampaloc or Lake Sampalok. It is the largest of the 7 lakes and is located in the center of the city, i.e., behind the city hall, and is dotted with fishpens and small cottages built on stilts for tilapia16, big head carp, and several species of freshwater fish like catfish (hito), ayungin17 and mudfish (dalag), as well as shrimps.

Lake Sampaloc – Source of photos: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/
Its volcanic origin is attested by almost half of its depth which has a shallow depression at the bottom. It has a surface area of 104 ha (260 acres) with an average depth of 10 m (33 ft). It has a maximum width of 1.2 km (0.75 mi) and a maximum depth of 27 m (89 ft).
Legend goes that a tamarind (sampalok) tree once grew in the garden of a selfish, stingy, old woman. One day, an old man begged for some tamarind fruit as a cure for his ailing grandson but instead of helping him, the old woman released her ferocious dogs to drive him away. The old man was badly hurt, but he was actually a fairy (diwata) in disguise. When the old man departed, there was a thundering noise and rain, followed by the cracking of the earth. The entire orchard sank into a colossal pit which was immediately filled with water, which the villagers, henceforth, named the lake after the tree – sampaloc.
9. The sixth and seventh lakes are Lake Pandin and Lake Yambo, known as “Twin Lakes”. These lakes are located in Barangay San Lorenzo, and are separated only by a narrow strip of land.
Lake Pandin is said to be “the most pristine” of the 7 lakes and the best kept lake. It has an area of 20.5 ha, a maximum depth of 63 m, and a calculated volume of 6,600 m3 of water in storage. It has an abundant plant and fish life. This lake is also famous for swimming and lake tours.
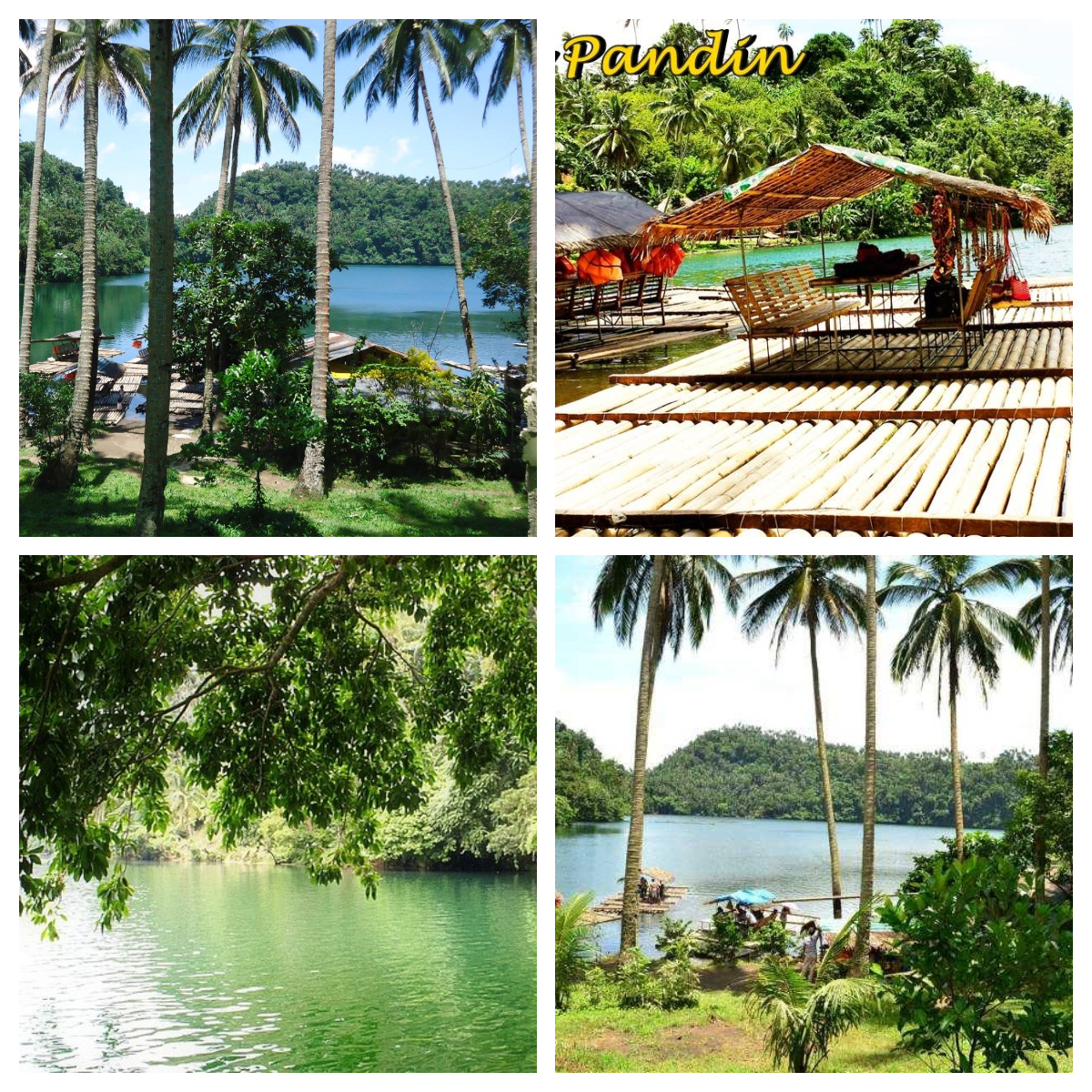

Lake Pandin – Source of photos: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/
You have to trek for about 20 minutes to reach this lake. You will pass by so many coconut trees and even a farm. When you reach the take-off point, register, pay PHP200 per person, and wait for your turn to ride an 8-person bamboo raft, good for a 2-hr ride. If you do not want to wait during your weekend or peak season visit, make a reservation.
While waiting, you can go around and buy some souvenirs, enjoy halo-halo18 or any snack or drink sold there, take pictures, and even find time to go to the rest room to prep for your two-hour ride. If there are less than 8 persons in your group, other visitors will be allowed to join your raft. Lunch (with bottled water) can be included in payment, for a total of PHP360. Life vests are provided. Fresh buko (coconut) is sold for PHP25.
The swimming area is shaded by a big tree with a swing. You are advised not to swim too far from the raft, and to always wear your life vest. Do not forget to have a picture taken while riding the swing.
Lake Yambo is a crater lake which has a surface area of 20.5 ha (51 acres) and an average depth of 63 m (207 ft). It is suitable for swimming, outings and picnics, just like its twin lake, Lake Pandin.
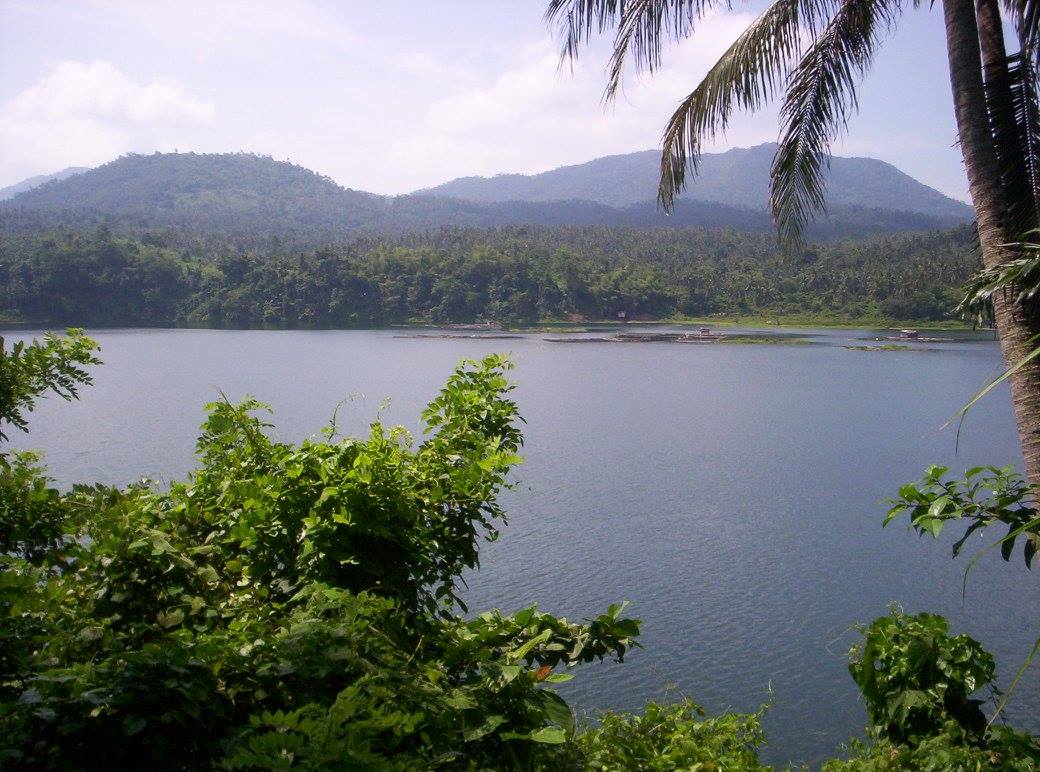

Lake Yambo – Photo source: https://www.facebook.com/CityOfSevenLakes4000Philippines/photos/a.1124214957663334/1124280190990144
There is also a legend about these twin lakes, named after two lovers. A beautiful lady, named Pandin, was cursed not to step on the earth, otherwise, something terrible would befall her. Yambo, her ardent lover, did not know about the curse, and made her step on earth, after which there was a terrible noise, followed by the cracking grumble of the earth, and a heavy downpour, which eventually converted the area into two lakes, separated from each other by a bare strip of land.
You need to cross Lake Pandin and hike about 3-5 minutes to reach the vantage point of Lake Yambo.
10. In 2005, the Rotary Club of San Pablo City held a ceremony that officially opened the hiking trails that connect the 7 lakes of the city. I cannot find a map, or any detailed information, of the hiking trails but will definitely update this post once I access such information.
11. Do you know how to get to San Pablo from Metro Manila? You can take a bus heading to Lucena from the bus terminals of Ali Mall (in Cubao, Quezon City) or Buendia. The ride is about 2 1/2 hours and costs about PHP200. You can be dropped off at San Pablo Medical, from where you would take a tricycle to Sampaloc Lake for about PHP50. From Sampaloc Lake, you can negotiate and hire a tricycle to take you to the rest of the lakes for around PHP600. If you have a vehicle, just use your GPS.
12. It is so sad that these lakes are threatened by human intervention and exploitation, most especially Lake Sampaloc since it is located in the center of the city. However, a bay walk and leisure park were constructed around this lake. Said bay walk and park are protected and maintained by the city government through regular Friday cleanup.
Illegal fish pens and settlements as well as commercial infrastructures on the shores have proliferated on some of the lakes, and caused increased pollution.
The city government has addressed the problem of the entry of invasive species and pollution in the seven lakes since 1992, according to the City Environment and Natural Resources Officer Ramon de Roma.
Demolition and different ecological conservation were implemented by both government and non-government organizations in recent years. The city government has carried out its lake clean-up program which was initially funded by the Office of the President, enforced and sustained by the Fisheries and Aquatic Resources Management Council, and participated by multi-sectors groups.
The information was obtained from https://llda.gov.ph/seven-7-crater-lakes/, https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1060191, https://www.facebook.com/7-Lakes-of-San-Pablo-City-Laguna and the Wikipedia pages “Seven Lakes of San Pablo”19, “Lake Bunot”20, “Lake Calibato”21, “Lake Muhikap”22, Lake Palakpakin”23, “Lake Sampaloc”24, and “Lakes Pandin and Yambo”25.
So there you have it, nature lovers! A trip to San Pablo’s 7 lakes will surely uplift your spirits. Remember to reserve ahead of time, especially during weekends and peak season.
Here are some tips:
- Wear light clothes for short trekking.
- Bring swim wear and extra clothing.
- Fully charge your cellphones, cameras, GoPro, charger/s, etc.
- Visit this Facebook account: https://www.facebook.com/enchantinglakemohicap/?ref=page_internal. Get the contact number, and be sure to reserve, at least 3 days before your expected arrival so food can be part of your tour.
Let us recap. You can go swimming and rafting. There are life vests for those who do not know how to swim.
You can rent a bike or a bicycle with a sidecar (for your companion, if any) and go from one lake to another. You can also rent fishing rods and catch your own fishes.
If you are lucky and visit early, you can also witness fishermen in action and buy their fresh catch. You can also camp around the lakes, just ask from the designated locations.
You can also trek or jog along the lakes to finish your exercise or 10,000-step goals for the day! Of course, you can try their lomi26, halo-halo18 and whatever else they sell during your visit. And, while you are in Laguna3, go to nearby attractions to maximize your stay there. You can visit http://www.sanpablocitygov.ph/ or the websites of the other nearby towns and the Laguna website for other attractions.
This is not a sponsored post. I just want my readers to know more about the Philippines.
Did you find this post informative? I would like to hear your comment/s regarding the 7 lakes of San Pablo, especially if you were able to see them.
See other interesting places through other posts in this category and other categories of SCapades, Pinoy Delights, and Smart Traveler – Now You Know, Short and Simple, and Say, Say, Say. Happy reading, and I hope that you will appreciate what I shared and some of the featured destinations will be part of your future travel plans!
Remember to share this post with your friends, follow me by clicking on the bottom right corner of your device, and do not forget to like this post. Thank you.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
The following terms are defined for interested readers, especially those with “Senior-Moments”, those not familiar with Filipino terms, and those too busy or lazy to Google such terms:
1The City of San Pablo is a first class city in the province2 of Laguna3, in the Calabarzon4 region5 of Luzon6, in the Philippines. It is one of the oldest cities in the country, and by land area, it is the largest in the province. It is called the “City of Seven Lakes”, referring to Lakes Bunot, Calibato, Muhikap, Palakpakin, Pandin, Sampaloc, and Yambo.
It was founded in 1586, chartered in 1647, and became a city on May 7, 1940. It has 80 barangays27.
The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “San Pablo, Laguna.”28
2A province is the primary administrative and political division in the Philippines. It is the second-level administrative sub-division of a region5. There are 81 provinces (called lalawigan) in the Philippines. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, and by an elected governor. Remember, a province in the Philippines is divided into cities and towns (called municipalities29), which in turn, are divided into barangays27, formerly called barrios. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Provinces of the Philippines.”30
See a related post: Foreign Seniors Ask: WHAT ARE PROVINCES IN THE PHILIPPINES?
3Laguna is a province2 in the Calabarzon4 Region5 of the Philippines, located southeast of Metro Manila, north of the province of Batangas, west of the province of Quezon, south of the province of Rizal, and east of the province of Cavite. This is the 7th richest province in the country, and the third largest province in the region. It hugs the southern shores of Laguna de Bay, the largest lake in the country. It is composed of 24 municipalities29 and 6 cities. The provincial capital is the town of Santa Cruz since 1858, after Bay (1581-1688) and Pagsanjan (1688-1858). It is historically one of the first provinces in the Philippines to have been visited by Christian missionaries. Its main natural resources are its agriculture and fisheries, owing to its position near Laguna de Bay and the surrounding lowlands. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Laguna (province)”.31
4Calabarzon, or Region IV-A, or Southern Tagalog Mainland, is a Philippine region5 located in the island group of Luzon6, with the city of Calamba as its regional center. CALABARZON is an acronym for this region’s five provinces2: CAvite, LAguna3, BAtangas, Rizal, QueZON. It is the most populated region in the country and the country’s second most densely populated region, after Metro Manila. This region is located south of the National Capital Region (NCR), bordered by the provinces of Aurora, Bulacan, and Metro Manila in the north, Manila Bay in the west, Tayabas Bay, and Sibuyan Sea in the south, and Lamon Bay, and the Bicol Region in the east. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Calabarzon”32 and https://lga.gov.ph/region/region-iv-a.
5A region is an administrative division based on geographical, cultural and ethnological characteristics. Each region is further subdivided in provinces2, composed of cities and municipalities29 (or towns), which in turn, are divided into barangays27, formerly called barrios, according to Wikipedia page “Regions of the Philippines” 33.
See a related post: Foreign Seniors Ask: WHAT ARE THE REGIONS OF THE PHILIPPINES?
6Luzon is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. It is ranked the 15th largest island in the world by land area, at 109,964.9 sq.km. (42,457.7 sq mi). It is the northern portion, among the three primary island groups in the Philippine archipelago, with Visayas at the center, and Mindanao at the southern part. It is the economic and political center of the country, with Manila as the capital city, and Quezon City as the country’s most populous city. It has a population of 53 million, as of 2015, representing 52.5% of the country’s total population, and the fourth most populous island in the world. The name Luzon comes from the Tagalog word lusong, a large wooden mortar used to de-husk rice. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Luzon”.34
7A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagnetic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes in contact with hot lava or magma). It characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow crater lake which may also be called a maar.
This shallow, flat-floored crater is a result of a violent expansion of magmatic gas or steam. It ranges in size from 60 to 8,000 m (200 – 26,250 ft) across, and from 10 to 200 m (33 – 656 ft) deep. It is commonly filled with water to form natural lakes. It usually has a low rim composed of a mixture of loose fragments of volcanic rocks.
The name comes from a Moselle Franconian dialect word used for the circular lakes of the Daun area of Germany.
The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Maar.”35
8The San Pablo Volcanic Field, or the Laguna Volcanic Field, is an active volcanic field in the Philippines, located between Laguna de Bay, Mount Banahaw13 volcano complex and Mount Malepunyo36 range. It is part of the larger Southwestern Luzon Volcanic Field (SWLVF).
The field is composed of over 200 dormant and monogenetic9 maars7, crater lakes, scoria cones37, and stratovolcanoes38, the tallest of which is Mount Makiling12 at 1,090 m (3,580 ft) in elevation. The oldest sediment-filled maars are found in the town of Calauan in Laguna3, while the youngest maars are concentrated in San Pablo City1.
The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Laguna Volcanic Field.”39
9Monogenetic means a maar9 or volcano erupted only once, as opposed to polygenetic, which means erupting repeatedly over a period of time, according to the Wikipedia page “Monogenetic volcanic field”40.
10The Macolod Corridor is an area, around 40 km wide, in southwestern Luzon6, with still active intense Quarternary volcanism which perpendicularly crosses Luzon in a NE-SW direction. The tectonic setting of this corridor is still somewhat questionable due to several, not yet understood, major structural elements affecting southwestern Luzon. Based on available information, it is believed that this corridor is a pull-apart zone formed by a diffuse system of NW-SE oriented shearing.41
11A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes where a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into 2 or 3 well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent, believed to be primarily caused by internal and gravitational stresses generated by magma emplacement within and across various regions of the volcano.
It allows the intrusion of magmatic dykes to flow into a crack on the slope of the volcano which eventually solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. The accumulated lava of repeated eruptions from rift zones, along the endogenous growth created by magma intrusions causes these volcanoes to have an elongated shape.
The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Rift zone.”42
12Mount Makiling, or Mount Maquiling, is an inactive stratovolcano38 located in the provinces2 of Laguna3 and Batangas, on the island group of Luzon6, Philippines. It rises to an elevation of 1,090 m (3,580 ft) above mean sea level, and is the highest feature of the Laguna Volcanic Field. This volcano has no recorded historic eruption, but volcanism is still evident through geothermal features like mud spring and hot springs.
Mount Makiling National Park is the first national park of the Philippines. It was established on February 23,1933 by Proclamation No. 552. It was then decommissioned as a national park on June 20,1963 by Republic Act. No. 3523, when it was transferred to the University of the Philippines Los Baños for use in forestry education and information. So, it is currently a state-owned forest reserve administered by the said university.
This mountain is sacred to many pilgrims, and is widely believed to be the home of Makiling, a goddess sent by the Tagalog43 supreme deity Bathala to aid mankind in the area. It is highly associated with the gifts of nature. Due to its importance, various sects have made the mountain an annual pilgrimage site. It was also declared as an ASEAN Heritage Park44 on September 25, 2013, with the title of “Mount Makiling Forest Reserve”.
The information was obtained from Wikipedia pages “Mount Makiling”45 and “Indigenous Philippine shrines and sacred grounds”46.
13Mount Banahaw is an active, three-peaked volcano located between the provinces2 of Laguna3 and Quezon, in the island of Luzon6, in the Philippines. It is the tallest mountain in the Calabarzon4 region5, with an elevation of 2,170 meters, so it is a favorite among mountain climbers. It is also considered a “sacred mountain” and pilgrims visit its sacred springs, caves, streams and boulders. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Mount Banahaw”.47
14A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption resulting from interaction between magma and water, according to the Wikipedia page “phreatomagmatic eruption”.48
15Mount San Cristobal is a potentially active volcano at the boundary of the provinces2 of Laguna3 and Quezon, on the island of Luzon6, Philippines. Its northern slope is bordered by city of San Pablo1, and its southern slope, by the municipality29 of Dolores. It has an elevation of 1,479 meters (4,820 feet) above mean sea level. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Mount San Cristobal.”49
16Tilapia is a freshwater fish which inhabits shallow streams, ponds, rivers and lakes in temperate countries. In the Philippines, it is commonly called pla-pla, and several species of tilapia are commercially grown in major lakes and rivers like Laguna de Bay, Taal Lake and Lake Buhi. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Tilapia”.50
17Ayungin, bagaong, bigaong, bugaong, or silver perch, is a species of fish in the family of Terapontidae, the grunters. Leiopotherapon plumbeus, its genus-species name, is endemic to the Philippines and reaches 16 cm in maximum length. Would you believe that the male of the species is the one who guards and tends the eggs?
This fish is caught and consumed locally as food. It is considered to be one of the most delicious of the native freshwater fish in the country. However, it is now rare and expensive since its population was greatly declined due to overharvesting.
The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Leiopotherapon plumbeus”.51
18Halo-halo, or haluhalo, is a popular cold dessert or snack in the Philippines made of crushed ice, evaporated milk or condensed milk, and various ingredients like different kinds of sweetened beans, ube (purple yam), coconut strips, gulaman (agar), sago (tapioca pearls), pinipig (toasted, pounded immature grains of glutinous rice), topped with leche flan (Philippine creme caramel). Other ingredients used are fruit slices, sweetened langka (jackfruit), boiled and cubed taro, and soft cubed yams. For a special treat, a scoop of ice cream, preferably ube, tops this dessert. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Halo-halo”.52
19“Seven Lakes of San Pablo,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven_Lakes_of_San_Pablo
20“Lake Bunot,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lake_Bunot
21“Lake Calibato,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lake_Calibato
22“Lake Muhikap,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lake_Muhikap
23“Lake Palakpakin,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lake_Palakpakin
24“Lake Sampaloc,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lake_Sampaloc
25“Lakes Pandin and Yambo,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lakes_Pandin_and_Yambo
26Lomi, or pancit lomi, is a Filipino dish made with a variety of thick fresh egg noodles, sauteed thinly sliced pork (or chicken) and pork liver, soup stock, chopped cabbage, seasoned as desired, and thickened with a slurry. Just before serving steaming hot, in individual bowls, a beaten egg is added while continuously stirring to complete this dish. Toppings are added like slices of kikiam53, fish balls, cooked shrimp, meatballs, chives, stir-fried pork or chicken, and coarsely ground roasted garlic. A spicy condiment can be provided, consisting of a mixture of soy sauce, calamansi (Philippine lime) juice and crushed fresh red chili peppers. Some people request a small amount of finely chopped fresh red onions for extra pungency. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Lomi”.54
27A barangay is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines, headed by a barangay captain, aided by a Sangguniang Barangay (Barangay Council). It is the native Filipino term for a district or village. It was formerly called a barrio. In a metropolitan area, a barangay is an inner city neighborhood, a suburb, or a suburban neighborhood. The word barangay originated from the term balangay, a kind of boat used by a group of Austronesian people who migrated to the Philippines. A number of barangays grouped together is called a district. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Barangay.”55
28“San Pablo, Laguna,” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/San_Pablo,_Laguna
29A municipality is a small, single urban administrative division, or local government unit (LGU)56, in the Philippines which has corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by law. It is a unit under a province2, subdivided into barangays27, and is called town, or bayan. In the Philippines, a municipality is headed by a mayor, a vice mayor and members of the Sangguniang Bayan (legislative branch). The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Municipalities of the Philippines.”57
30“Provinces of the Philippines,” accessed July 17, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Provinces_of_the_Philippines
31“Laguna (province),” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laguna_(province)
32“Calabarzon,” accessed March 2, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calabarzon
33“Regions of the Philippines,” accessed July 17, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regions_of_the_Philippines
34“Luzon,” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luzon
35“Maar,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maar
36Mount Malepunyo is an extinct volcano which is the highest peak (among 3) of the Malepunyo Range, located in Barangay27 Talisay, Lipa City, in the province2 of Batangas, Philippines. It is 1.002 m (3,287 ft) above mean sea level by the ridge of its caldera. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Malepunyo Mountain Range.”58
37A cinder cone, scoria cone, or scoria mound, is a small, steep-sided volcanic cone built of loose pyroclastic59 fragments. As gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall either as volcanic clinkers, cinders, volcanic ash, or scoria60 around the vent to form a cone that often is beautifully symmetrical, with slopes between 30 and 40°, and a nearly circular ground plan. It has a basal diameter of 800 meters (2,600 ft.) and range from 250-2,500 meters (820-8,200 ft.). It rarely rises more than 50-350 meters (160-1,150 ft.) or so above its surroundings. It typically has a bowl-shaped crater at the summit, with a diameter ranging between 50 and 600 meters (160 and 1,970 ft.). It is usually active for very brief periods of time before becoming inactive. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Volcanic cone”.61
38A stratovolcano is a conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened ash, lava, pumice and tephra62. It has a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive and effusive eruptions, but some may have collapsed summit craters called calderas. Its lava flow typically cools and hardens before spreading far due to high viscosity, but extensive felsic lava63 flows may travel up to 15 km (9.3 miles). It is sometimes called a composite volcano because of its composite stratified structure built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. Examples are Mount Pinatubo (also in the Philippines), Krakatoa (Indonesia) Mount St. Helens (USA) and Mount Vesuvius (Italy). The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Stratovolcano”.64
39“Laguna Volcanic Field,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laguna_Volcanic_Field
40“Monogenetic volcanic field,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monogenetic_volcanic_field
41https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/004019519090420D
42“Rift zone,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rift_zone
43Tagalog refers to the second largest ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines, after the Visayan people, numbering around 30 million, with most of them inhabiting Metro Manila, the Calabarzon4 region5 in southern Luzon6, the islands of Marinduque and Mindoro in Mimaropa, as well as a plurality in the provinces2 of Aurora, Bataan, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija and Zambales in Central Luzon. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “Tagalog (people).”65
44An ASEAN Heritage Park is a selected protected area in the ASEAN region which is known for its unique biodiversity and ecosystems, wilderness and outstanding values in scenic, cultural, educational, research, recreational and tourism. This was started by ASEAN on November 29, 1984, and as of February 18, 2021, there are 50 such parks. The information was obtained from Wikipedia page “ASEAN Heritage Parks.”66 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASEAN_Heritage_Parks for the complete list.
45“Mount Makiling,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mount_Makiling
46“Indigenous Philippine shrines and sacred grounds,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indigenous_Philippine_shrines_and_sacred_grounds
47“Mount Banahaw”, accessed March 1, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mount_Banahaw
48“Phreatomagmatic eruption,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phreatomagmatic_eruption
49“Mount San Cristobal,” accessed March 29, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mount_San_Cristobal
50“Tilapia,” accessed December 12, 2018, https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tilapia
51“Leiopotherapon plumbeus,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leiopotherapon_plumbeus
52“Halo-halo,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Halo-halo
53Kikiam, a popular street food in the Philippines, is a crispy mini meat-roll, sliced diagonally, skewered and served with your choice of sauces: spicy, sweet, or sweet-sour. It is made of seasoned ground pork and minced shrimp, or ground fish (turned into a paste), steamed, then deep-fried. It is peddled in wooden carts along streets with high traffic, along with street food like fish balls and squid balls.
54“Lomi,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lomi
55“Barangay,” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barangay
56A local government unit (LGU) in the Philippines is divided into 3 levels: provinces2, cities and municipalities29; and, barangays27, according to Wikipedia page “Local government in the Philippines”.67
57“Municipalities of the Philippines,” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Municipalities_of_the_Philippines
58“Malepunyo Mountain Range,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malepunyo_Mountain_Range
59A pyroclastic flow, pyroclastic density current, or pyroclastic cloud, is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra62) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at velocities of 100 km/h (62 mph) on average but is capable of reaching speeds up to 700 km/h (430 mph), with temperatures reaching 1,000°C (1,830°F). It is the most deadly of all volcanic hazards, and is produced as a result of certain explosive eruptions. It normally touches the ground and hurtles downhill, or spreads laterally under gravity. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Pyroclastic flow”.68
60Scoria is a highly vesicular, dark colored (brown, black, or purplish red) volcanic rock that may or may not contain crystals (phebocrysts). The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Scoria”.69
61“Volcanic cone,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volcanic_cone
62Tephra is a fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption, regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. The information was obtained from the Wikipedia page “Tephra”.70
63Felsic lavas are thick and gooey lava, not as hot as mafic lava, high in silica and volatiles, and resist flowing. Their high volatile content makes them potentially highly explosive. Most are extremely viscous and typically fragment as they extrude.
64“Stratovolcano,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stratovolcano
65“Tagalog people,” accessed January 15, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tagalog_people
66“ASEAN Heritage Parks,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASEAN_Heritage_Parks
67“Local government in the Philippines,” accessed April 2, 2018, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_government_in_the_Philippines
68“Pyroclastic flow,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyroclastic_flow
69“Scoria,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scoria
70“Tephra,” accessed May 28, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tephra

